Introduction to Oracle GoldenGate
- It is the strategic replication tool for Oracle database and also for Heterogeneous databases. It means data can be replicated to one another, independent of the database platforms.
- It is a strategic solution for Real Time Data Integration.
- It enables mission critical systems to have continuous availability and access to real-time data.
- It offers a fast and robust solution for replicating transactional data between operational and analytical systems.
Evolution of Oracle GoldenGate
- GoldenGate was founded in 1995 in San Francisco. The company was named after the famous Golden Gate Bridge by its founders, Eric Fish and Todd Davidson.
- Later In 2009, Oracle acquired the company GoldenGate and so it was called as Oracle GoldenGate.
- GoldenGate was Originally designed for the fault tolerant Tandem computers, the resilient and fast data replication solution was in demand.
- The banks initially used GoldenGate software in their ATM networks for sending transactional data from high street machines to mainframe central computers.
Key Features Of Oracle GoldenGate
- Supports Heterogenous Replication.
- High Performance. Able to replicat large volume of data very efficiently with low lag time.
- High Availability.
- Reliable and Extremely Resilient to failure and data loss.
- Zero-DownTime for Upgrades, Migrations and Maintenance
- Operational Business Intelligence (BI).
- Live Reporting System.
- Can be a Disaster Recovery.
- Flexible Architecture.
- Real Time Data Integration. Data is replicated in real-time.
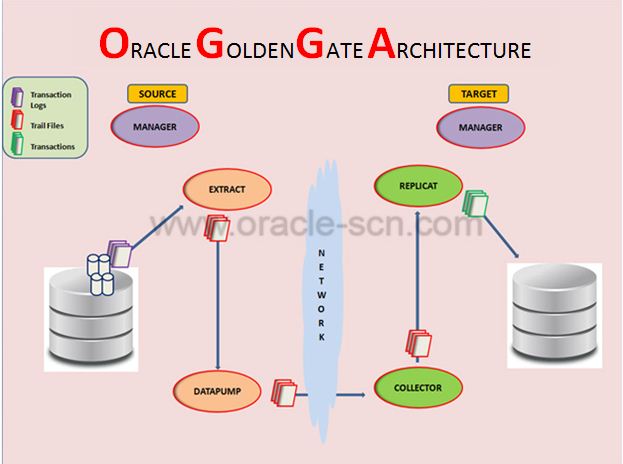
Architecture / Components of Oracle GoldenGate
- Manager Process
- Extract or Capture Process
- Data Pump Process
- Collector Process
- Replicat or Apply Process
- Trail Files
Manager Process
- It is the process which manages all the sub processes of the Oracle GoldenGate.
- The Manager process should be started and running on both the Source and Target Systems.
- This is the process which should be started initially and firstly on the system before starting any other goldengate processes.
- It performs a number of functions including monitoring and starting other GoldenGate processes, managing the trail files and also reporting.
Extract or Capture Process
- Extract process runs on the Source System.
- This process is responsible of capturing changed data from the database.
- Extract is not only used for capturing DML changes but also DDL changes happening in the database.
- It performs a number of functions including monitoring and starting other GoldenGate processes, managing the trail files and also reporting.
Data Pump Process
- It is a process which exists on the Source System.
- This process is also called as Secondary Extract process.
- The main work of this process is, it reads the data from the Local Trail File and pumps to the Target System via TCP/IP.
- This process is an Optional One.
Collector Process
- It is a background process which runs on the Target System.
- It receives the changes from the Source System and writes it to the Trail File.
- This process is started automatically by the Manager process and known as Dynamic Collector.
- It can also be started manually and so called Static Collector.
Replicat or Apply Process
- The Replicat process runs on the Target System.
- This process reads the Transactional Changes as well as DDL changes and applies these changes to the Target System.
- Multiple Replicat process can be configured in order to increase the performance of the Apply.
Trail Files
- Trail files are the temporary files where the changed data are read from and written to it.
- It resides in the disk.
- Extract process writes the captured data change to the trail files.
- The Replicat process reads the changed data from the trail files.
- The files which are present in the Local or Source Systems are called Local Trails.
- The files which are present in the Remote or Target Systems are called as Remote Trails.
Supported Topologies or Architecture Flexibility
- One to One
- One to Many
- Many to One
- Cascading or Downstream
- Bi-Directional Active-Passive
- Bi-Directional Active-Active
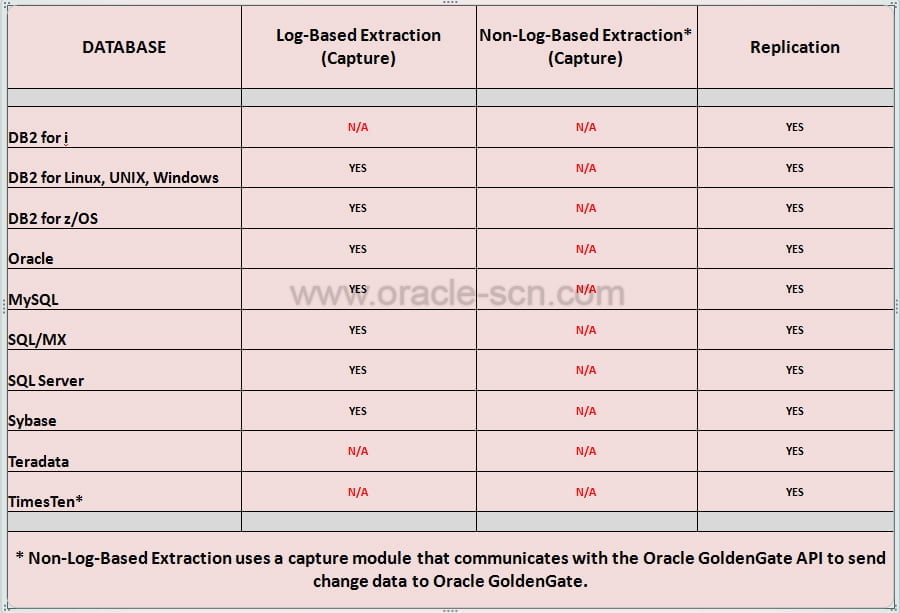
Supported Database Platforms and Replications



 Total Users : 1846429
Total Users : 1846429
Nice Article on Oracle Golden Gate
Thank You Renny..
Nice article
Nice articals given on Ogg ,thanks bro